The benefits of using synthetic data in cybersecurity

You've heard it before - data is the new water. In today's digital landscape, data is essential for everything from product development and marketing to security and compliance. The more data you have, the more opportunities you have to innovate, adapt, and grow.
However, as many organizations are still discovering, data compliance and security can pose significant challenges. Strict regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) require organizations to protect sensitive data at all times, while increasingly sophisticated cyber threats pose an ongoing threat to unprotected information.
According to McKinsey's global survey, cybersecurity remains the most recognized risk to data compliance, with 57% of responders citing it as a number 1 concern, followed by maintaining data privacy and protecting customer information.
Phishing campaigns, deceptive domains, and malicious apps are just a few examples of the types of cyberattacks that can easily compromise sensitive information. And with more people working remotely or online post-2020, cybercriminals are quadrupling the number of attacks they use to disrupt online activities.
So, how can organizations effectively manage their data, protect it from cyber threats, comply with strict regulations, and minimize the cost of data breaches?
What if they can identify the sensitive data within their organization, replicate its structure and features, and ensure it provides the same insights and value without leading back to a real person, identity, or business?
By doing so, the company's data would be useless to cybercriminals, insider threats, and regulation scope. It would eliminate a huge chunk of your data security and compliance headache while enabling more efficient analytics and product developments.
This is the power of using synthetic data.
What is synthetic data?
In a nutshell, synthetic data is artificial data generated by an AI algorithm from scratch to replicate the structure and features of real-world data. To generate it, organizations need to collect real data, add it to a machine learning model that captures its patterns, and generate synthetic data that mimics the structure and features of real-world data while removing all identifying information.
The goal is to replicate real data's statistical properties and patterns while stripping it of any identifying information that would make it usable in a real-world scenario. Synthetic data is brand-new data with all the same properties and value as real-world data but doesn't come with the same risks, restrictions, or costs.
If generated thoroughly, it contains no personally identifiable information nor poses a risk to privacy or security. It's not subject to any regulations that would restrict its use. And most importantly, it doesn't come with the high cost of data breaches. Synthetic data removes the privacy and security headaches associated with real data while providing the same benefits.
By using synthetic data, smaller organizations compete with the big players when it comes to data, analytics, and product development. They generate synthetic datasets that outsize their original customer base, create advanced analytics that rivals those of big data companies, and enable new product developments based on real customer insights.
Synthetic data is indistinguishable from real-world data and can be scaled, modified, traded, and shared - allowing organizations to benefit from the power of data without the cost, headaches, or risks. And as cybersecurity threats continue to evolve, organizations that use synthetic data will be able to stay ahead of the curve and protect their data from cyber threats.
To learn more about synthetic data, how to generate it, and how to determine its quality, visit our guide - Synthetic Data 101.
What are the benefits of synthetic data in cybersecurity?
The main benefits of using synthetic data in cybersecurity are:
- Reducing the risks of privacy and security breaches
- Improving analytics and data-sharing capabilities
- Staying compliant with regulatory requirements
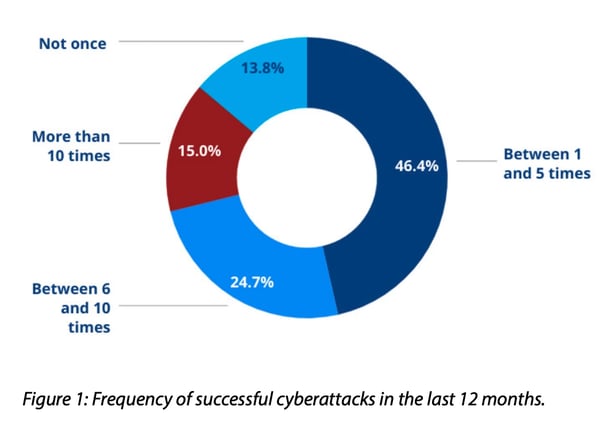
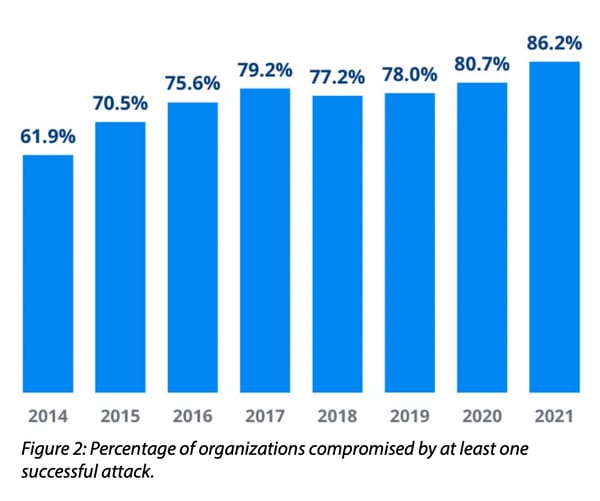
A global 2021 Cyberthreat Defense Report shows how vulnerable organizations have become to cyber-attacks and what the root causes are. Just over 86% of the responding organizations experienced at least one successful cyberattack within the preceding 12 months, with about four in 10 organizations experiencing six incidents or more.
In 2020 successful cyberattacks crossed the 80% threshold for the first time in the report's history. In 2021, the largest annual increase in successful attacks occurred within the last six years.
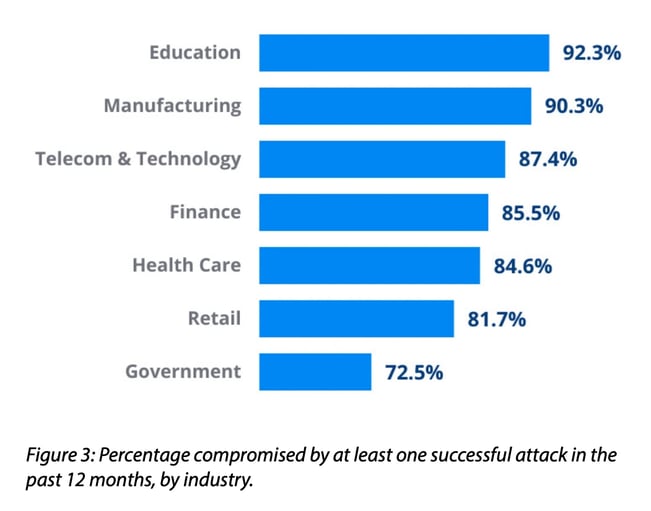
Of the seven major industries surveyed for this report, education was the hardest hit, with 92.3% of organizations reporting a successful attack, followed by manufacturing (90.3%), telecom and technology (87.4%), and finance (85.5%). Next came healthcare (84.6%), retail (81.7%), and government, with only 72.5% of respondents experiencing a successful attack.
While a combination of policies, protocols, and cybersecurity tools is crucial for safeguarding sensitive data, the risk of using that data still won't be entirely eliminated. Organizations that rely solely on their original sensitive data face legal troubles and reputation damages if that data happens to be misused or compromised.
By leveraging synthetic data in cybersecurity, organizations can mitigate these risks by creating realistic data sets that are more difficult for cybercriminals to identify and misuse while also improving their ability to detect, predict, and mitigate cyberattacks. Additionally, synthetic data can help companies meet compliance requirements, such as those outlined in General Data Protection Regulation and Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act.
Synthetic data can populate data warehouses or sandboxes, run analytics like Machine/Deep Learning, serve as test data for product development, and share internally or externally while staying fully compliant.
Synthetic data vs. real data in cybersecurity
There are pros and cons to using both synthetic and real data in cybersecurity. Real data can provide more accurate, representative results, but it is difficult to obtain and puts sensitive or private information at risk. On the other hand, synthetic data is more reliable and consistent since it's generated algorithmically rather than based on actual user or system behavior. This makes it less prone to errors and biases arising from human input or questionable datasets. In addition, synthetic data is often easier to create and manage, making it a more scalable and cost-effective solution for organizations of all sizes.
However, using synthetic data in cybersecurity can come with certain drawbacks. For example, some types of synthetic data, such as images or audio recordings, may be challenging to generate reliably and may contain errors or inaccuracies that can affect the quality of results. Additionally, synthetic data may not accurately model a specific scenario or user activity, and it may be difficult to reproduce the same results multiple times, which could hinder your ability to detect and mitigate cyberattacks effectively.
Ultimately, the best approach to cybersecurity depends on the needs and goals of your organization. If you want reliable, consistent results that are easier to create and manage without compromising the privacy of your users, synthetic data is the right choice for you.
The average cost of a data breach
There are seven common cyberattacks your organization may face:
- Malware Attacks
- Phishing Attacks
- Distributed Denial of Service Attacks (DDoS)
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
- Credential Stuffing Attacks
- Password Spraying Attacks
- Mobile Device Attacks
These attacks can have a significant financial impact on your organization, depending on the type and severity of the cyberattack. While there is no single "average" cost of a data breach, as the cost varies greatly depending on factors such as the size, industry, and type of organization affected, we can still learn a lot from historical data.
In 2017, nearly 197 million records were exposed due to data breaches. In 2020, that number grew to 37 billion, even though the overall number of data breaches had decreased. IBM reports that the costs are increasing for organizations that fall victim to these attacks in countries like the United States, where the average data breach cost increased from $7.91M to $8.64M between 2018 and 2020.
As of 2022, the average data breach cost in the United States amounted to 9.44 million U.S. dollars, up from 9.05 million U.S. dollars in the previous year. The global average cost per data breach was 4.35 million U.S. dollars in 2022.
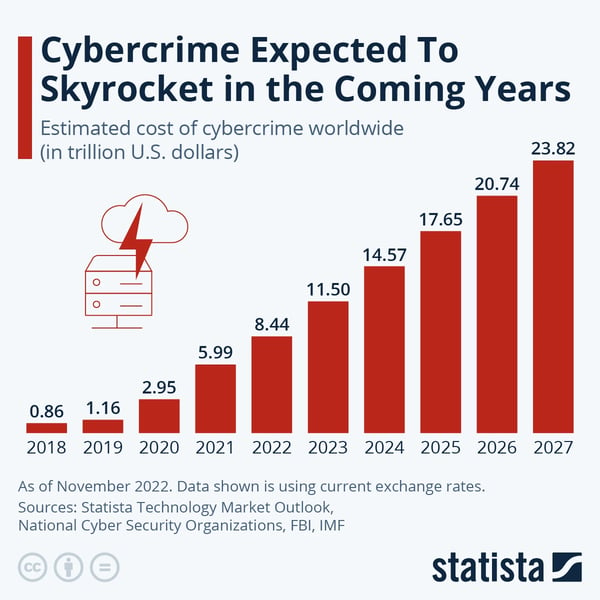
According to Statista, the worldwide cost of cybercrime will increase drastically over the following years, as shown in the figure below. These increasing costs highlight the importance of investing in robust cybersecurity measures to protect your data. While combining policies, protocols, and cybersecurity tools is crucial for safeguarding sensitive data, the risk of using that data still won't be eliminated.
How to use synthetic data to detect threats and prevent data breaches?
Synthetic data helps fortify internal security in the age of data breaches. Usually, the largest data security risk is employee misuse or abuse of raw or anonymous data. Using synthetic data to power security tools, you can effectively detect and prevent these threats by accurately identifying and flagging suspicious activity.
There are several key steps that you can take to leverage synthetic data in your cybersecurity strategy. First, it is essential to choose a high-quality, reliable source of synthetic data specifically designed for cybersecurity. This will ensure that your data is accurate, consistent, and easy to maintain over time.
Next, you can utilize a range of security tools powered by synthetic data, such as anomaly detection systems or machine learning models, to detect threats and prevent data breaches in real-time. These tools can give you greater visibility into suspicious activity and help you quickly identify threats that may be missed using traditional data sources.
Ultimately, by using synthetic data in your cybersecurity strategy, you can stay ahead of evolving threats and mitigate the risks associated with security breaches. With the right approach and tools, you can protect your organization from costly cyberattacks and keep your sensitive data safe and secure.
Examples of using synthetic data for cybersecurity
One of the key benefits of using synthetic data for cybersecurity is that it provides highly accurate insights into potential threats in real-time. By modeling possible threat scenarios using synthetic data, you can proactively identify suspicious activity and protect your IT systems from malicious attacks.
Some of the use cases of synthetic data in cybersecurity include:
Cracking passwords with synthetic data
Cracking passwords differs from guessing a web login password, which typically only allows a small number of guesses before locking your account. Instead, someone who has gained access to a system with encrypted passwords ("hashes") will often try to crack those to recover the original passwords. To do this, they will usually generate a large number of password guesses and try them all against the hashes in sequence.
One way to mitigate the risk of password cracking is to ensure passwords are no longer stored in plain text. Instead, they can be stored as hashes, where each hash uniquely represents the password.
But what if all you've got is the hash? Software applications like 'hashcat' can often help you recover a password because humans are somewhat predictable in their password choices. However, research shows that hashing alone is not sufficient to mitigate more involved attacks. A better way to store passwords is to add a 'salt' to the hashing process: adding additional random data to the input of a hashing function that makes each password hash unique.
With both hashing and salting, an attacker has no easy way to discover our original passwords. The benefit of using synthetic data in password hashing is that it can generate billions or even trillions of iterations, making it far more difficult for an attacker to crack even a single hash. This keeps your users' passwords secure and gives you the peace of mind of knowing that your systems are protected against modern cyberattacks.
Product testing with synthetic data
In 2020, a dozen enterprise security practitioners were solicited to determine the value on a scale of 1 through 5 for using synthetic datasets for cyber security product testing. The results averaged 3.85, corresponding to a favorable view of using synthetic datasets for cyber security product testing.
One of the key benefits of using synthetic data for product testing is that it allows businesses to identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. Companies can use synthetic datasets to replicate real-world attack scenarios, life-cycle testing, vulnerability testing, or fuzz testing. This helps to identify and mitigate issues with the software, hardware, or network infrastructure before they become a problem.
Intrusion detection with synthetic data
Synthetic data generation can support the dynamic generation of enticing content for intrusion detection. Such on-demand capability has the potential to drive honeypots from static, pre-determined entities into live, adjustable resources that can be crafted based on the behavioral attributes of the environment.
Detecting intrusions is a critical aspect of cybersecurity. Synthetic data can help detect these attacks by allowing businesses to identify unusual activity or suspicious behavior. By using synthetic data to create test profiles, simulations, and mock attacks, companies can effectively detect intrusions and take measures to prevent them from happening in the future.
Security awareness training with synthetic data
Synthetic data can support a variety of security training and compliance framework needs. Customer support representatives, for example, could use it to demonstrate their ability in a simulated data environment, using records that can't be differentiated from original data. Financial services organizations might use synthetic data to create textbook examples of unusual activity, demonstrating how to identify and report an incident.
Whether training new employees or ensuring that existing staff are up-to-date on the latest cybersecurity best practices, synthetic data can help businesses build and maintain a strong security culture. By creating realistic simulations and mock scenarios with synthetic data, companies can ensure that their employees have the knowledge and skills to protect their actual customer data and keep their systems secure.
Steganography resistance with synthetic data
Steganography is the process of hiding information in otherwise normal-looking files. For example, changing the least significant bit in each RGB pixel value of an image would allow information to be stored in the image file without altering its appearance to a human observer.
One potential drawback of using synthetic data for steganography is that these images are easy to detect. Because realistic synthetic images require sophisticated algorithms, it is relatively easy for cybersecurity systems to identify whether or not an image has been altered.
However, by using artificial intelligence or machine learning to generate realistic synthetic data and images, businesses can create steganography capable of evading detection. Results show that synthetically generated images work better for hiding information than real images. This makes synthetic data an effective tool for protecting sensitive information and ensuring the security of your systems.
Challenges and limitations of using synthetic data in cybersecurity
Is synthetic data the solution to all problems? Of course not. While there are many benefits to using synthetic data in cybersecurity, actual customer data is still the most preferred and trusted source of insights for businesses. But, because it's expensive, difficult to collect, sensitive, and time-consuming to keep current and relevant, many companies may be reluctant to use it.
Synthetic data is a promising solution to these challenges, but its use still has limitations.
The key challenges and limitations of using synthetic data in cybersecurity include the following:
- Limited availability of high-quality synthetic data sets for training models and building applications.
- Difficulty in estimating the accuracy of models and applications based on synthetic data.
- Potential for bias in generated synthetic data, which could impact the accuracy of security models and risk assessments.
- Misuse or malicious manipulation of synthetic data, which could potentially disrupt security models and risk assessments.
- Lack of skilled professionals who can effectively use synthetic data to improve cybersecurity and compliance efforts.
- Cost and resource limitations may prevent some companies from using synthetic data effectively.
While there are certainly challenges to using synthetic data in cybersecurity, these issues can be overcome with careful planning, collaboration, and continued investment in research and development. With the right tools, strategies, and expertise, businesses and data scientists can reap the many benefits synthetic data offers and improve their security posture for the long term.
Strategies for overcoming the challenges of using synthetic data in cybersecurity
Businesses can use several key strategies to overcome the challenges of using synthetic data in cybersecurity. They include:
- Investing in data science and artificial intelligence skillsets to improve the quality of generated synthetic data.
- Developing frameworks and standards for measuring the accuracy and reliability of synthetic data.
- Collaborating with cybersecurity experts and other stakeholders to ensure that models and applications based on synthetic data are free from bias and manipulation.
- Creating policies and procedures that govern the use, storage, and sharing of synthetic data to mitigate risks and prevent its misuse or malicious manipulation.
- Investing in new technologies and techniques that can further improve synthetic data generation, including generative adversarial networks (GANs) and reinforcement learning.
- Developing a robust roadmap for continuous improvement in the use of synthetic data based on real-world feedback and input from customers and other stakeholders.
As businesses grow in size and number of customers, the need for more reliable, efficient, and cost-effective cybersecurity solutions becomes increasingly important. Synthetic data has great potential to address many of the challenges facing today's cybersecurity efforts. With the right strategies in place, businesses can overcome the hurdles to effectively using synthetic data in their security protocols.
Looking to the future
Synthetic data has exciting potential for the future of cybersecurity. As more businesses embrace its use, alongside the significant advances in AI and other related technologies, synthetic data will continue to play an important role in strengthening cybersecurity efforts and improving business outcomes.
Syntheticus is a leading provider of synthetic data solutions dedicated to helping businesses address the challenges and limitations of using synthetic data in their cybersecurity efforts. Whether you are just starting to explore the benefits of synthetic data or looking for ways to improve your current use of this technology, our data scientists and security experts are there to help. To learn more, book a demo today or visit www.syntheticus.ai.
Tags:
Synthetic Data
December 22, 2022